Definition and Characteristics of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models are a type of financial and economic model that uses a large number of different scenarios to simulate possible future outcomes.
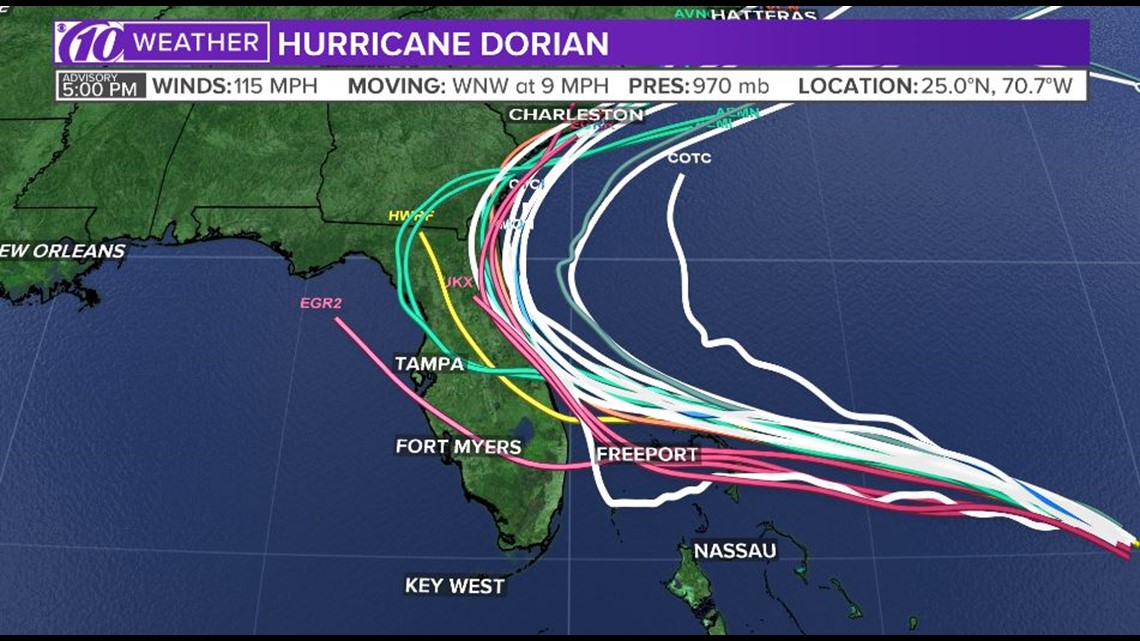
Spaghetti models, a tool for predicting hurricane paths, have been used to track the progress of the Jamaica hurricane. These models, which resemble spaghetti strands, show the possible paths a hurricane may take. While they can provide valuable information, it’s important to note that spaghetti models are only projections and should not be taken as absolute predictions.
Spaghetti models are characterized by their use of multiple simulations to generate a range of possible outcomes. This allows analysts to assess the sensitivity of their forecasts to different assumptions and inputs.
Spaghetti models, as they are colloquially known, are essentially a series of computer-generated maps depicting the possible paths of a hurricane. To get a clearer picture of this, take the example of Hurricane Beryl. By examining the path of hurricane beryl , we can see how spaghetti models can provide valuable insights into the potential trajectory of a storm, helping meteorologists make informed predictions and issue timely warnings.
Examples of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Forecasting economic growth
- Predicting the performance of financial markets
- Evaluating the risk of financial assets
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models, a type of financial model, offer both advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before use. Understanding these aspects can help users make informed decisions about the suitability of spaghetti models for their specific needs.
Advantages of Spaghetti Models
- Flexibility: Spaghetti models are highly flexible, allowing users to customize and adapt them to various scenarios and complexities. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of financial modeling tasks.
- Complexity Handling: Spaghetti models can effectively handle complex scenarios involving multiple variables and interdependencies. They provide a comprehensive approach to modeling financial situations that may be too intricate for simpler models.
Disadvantages of Spaghetti Models
- Complexity: The flexibility and complexity handling capabilities of spaghetti models can also be a disadvantage. The intricate nature of these models requires careful construction and interpretation to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Interpretation Challenges: Spaghetti models can be challenging to interpret, especially for users without sufficient financial modeling experience. The complexity of the models can make it difficult to understand the underlying assumptions and implications of the results.
Comparison to Other Financial Models
Compared to other types of financial models, spaghetti models offer a unique combination of flexibility and complexity handling. While simpler models may be easier to use and interpret, they may not be suitable for complex scenarios. On the other hand, more sophisticated models may offer greater accuracy but can be more difficult to customize and interpret.
Applications of Spaghetti Models

Spaghetti models are widely used in various financial and economic applications, offering unique insights and risk management capabilities. Their simplicity and flexibility make them particularly valuable in scenarios where complex relationships and uncertainty exist.
Risk Management
In risk management, spaghetti models are employed to assess and mitigate financial risks. They help identify potential sources of risk, estimate their impact, and develop strategies to manage them effectively. By simulating different scenarios and analyzing the resulting distributions, spaghetti models provide valuable insights into the likelihood and severity of potential losses.
Portfolio Optimization
Spaghetti models play a crucial role in portfolio optimization, where they are used to construct diversified portfolios that balance risk and return. By simulating different asset allocation strategies and analyzing the corresponding distributions, spaghetti models help investors identify portfolios that meet their specific risk-return preferences. They also assist in optimizing portfolio weights and identifying assets that contribute to diversification.
Forecasting, Spaghetti models
Spaghetti models are also used for forecasting financial and economic variables. They combine historical data with simulations to generate probabilistic forecasts that capture the uncertainty inherent in future events. By simulating different scenarios and analyzing the resulting distributions, spaghetti models provide insights into the potential range of future outcomes and help decision-makers prepare for various contingencies.
| Application | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management |
|
|
| Portfolio Optimization |
|
|
| Forecasting |
|
|